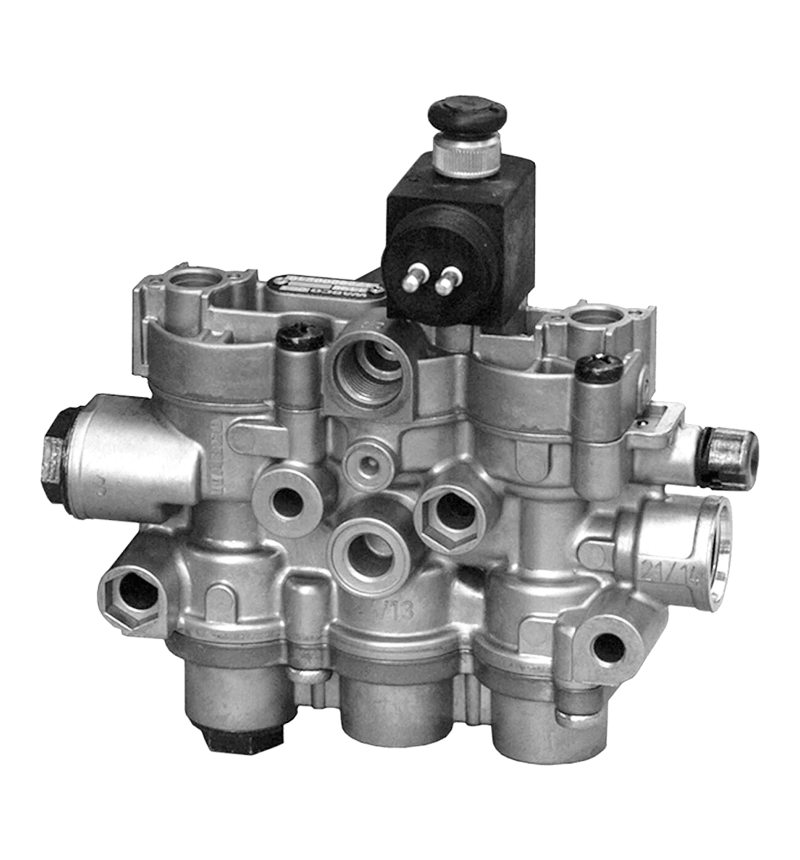
Working principle of solenoid valve
 2024.04.30
2024.04.30
 Industry News
Industry News
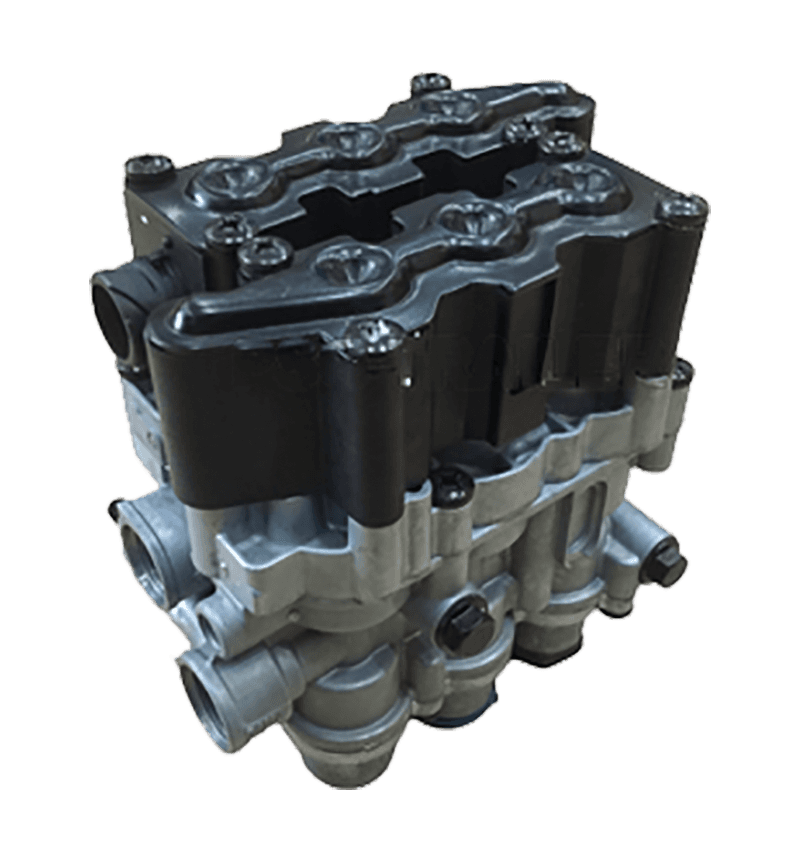
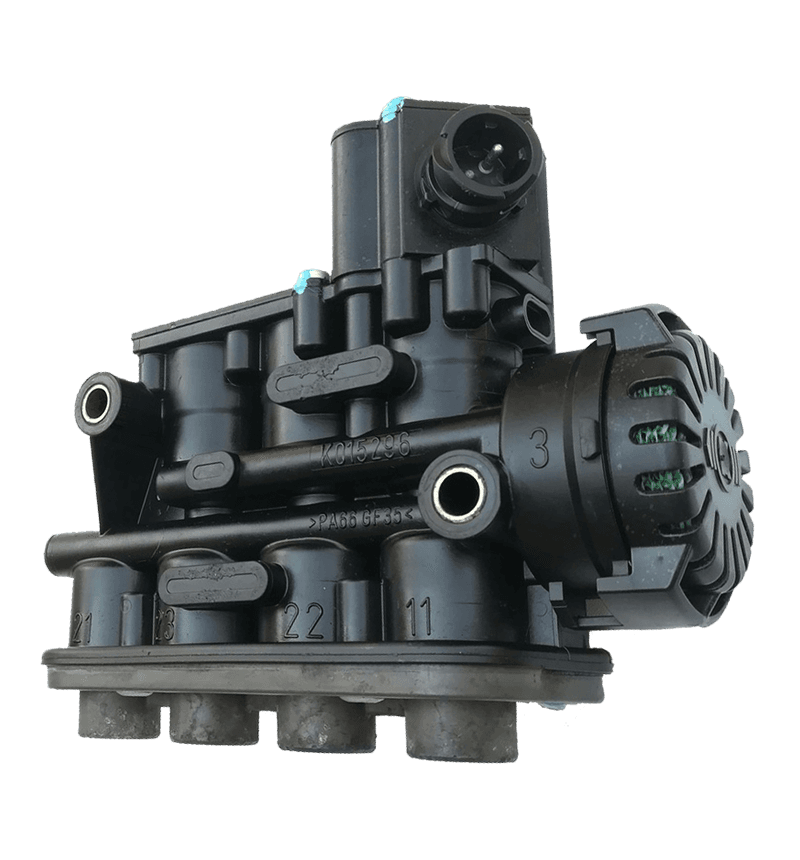
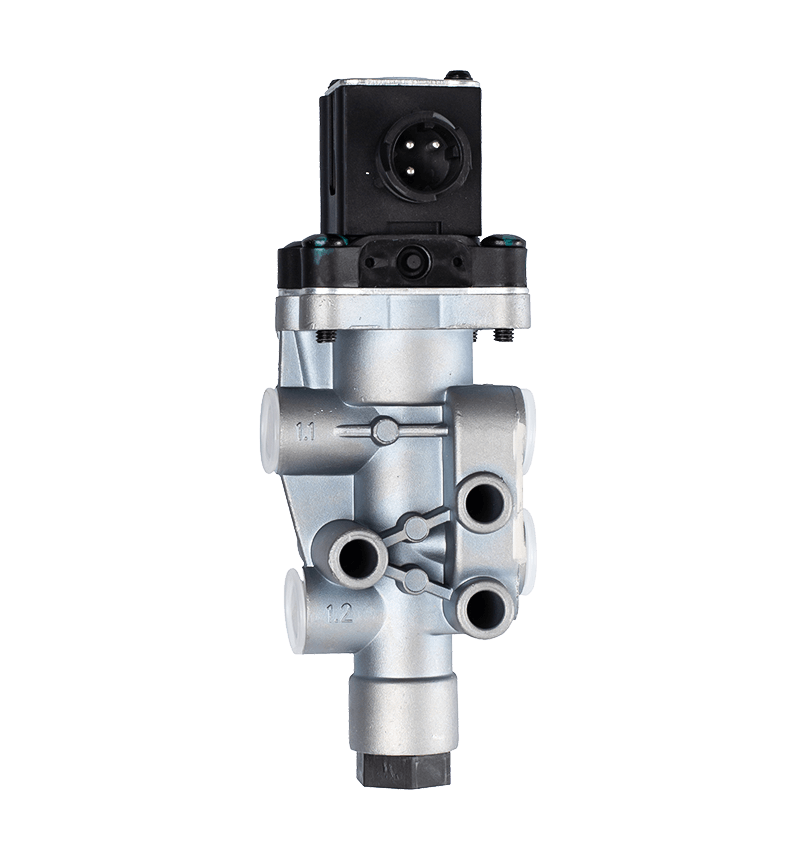
Electromagnetic valve is an automation component that uses electromagnetic control to control fluids, widely used in fields such as petrochemicals, power, chemistry, machinery, and scientific research. Its working principle is that the electromagnetic valve has a closed chamber inside, with through holes at different positions, each hole connected to different oil pipes (or gas pipes), a piston (or valve) in the middle of the chamber, and two electromagnets on both sides. The magnetic coil on which side is energized will attract the valve body to which side. By controlling the movement of the valve body, different oil (or gas) holes can be opened or closed. The oil (or gas) hole is normally open, and hydraulic oil (gas) will enter different oil (gas) pipes. Then, the pressure of the oil (gas) will push the piston (ignition needle) of the oil cylinder (furnace head), which in turn drives the piston rod, which in turn drives the mechanical device. In this way, mechanical motion is controlled by controlling the current flow of the electromagnet.
Electromagnetic valves can be divided into direct acting diaphragm structure, stepwise direct acting diaphragm structure, pilot diaphragm structure, direct acting piston structure, stepwise direct acting piston structure, and pilot piston structure based on the differences in valve structure, materials, and principles. Moreover, according to different functions, solenoid valves can be divided into various types such as water solenoid valves, steam solenoid valves, refrigeration solenoid valves, low-temperature solenoid valves, gas solenoid valves, fire solenoid valves, ammonia solenoid valves, gas solenoid valves, liquid solenoid valves, micro solenoid valves, etc.

 English
English Español
Español