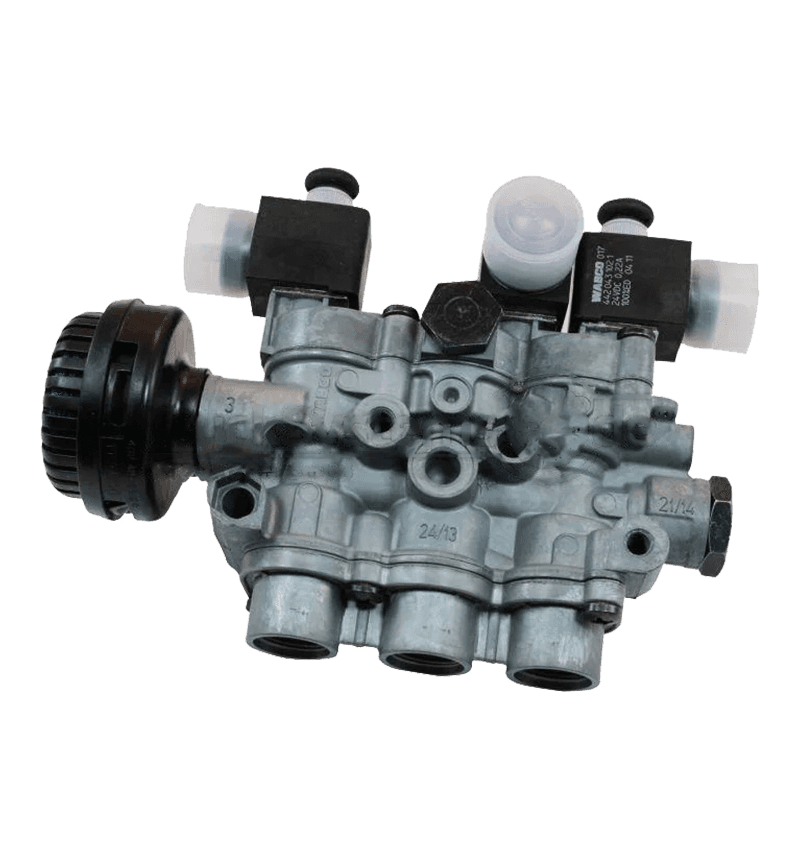
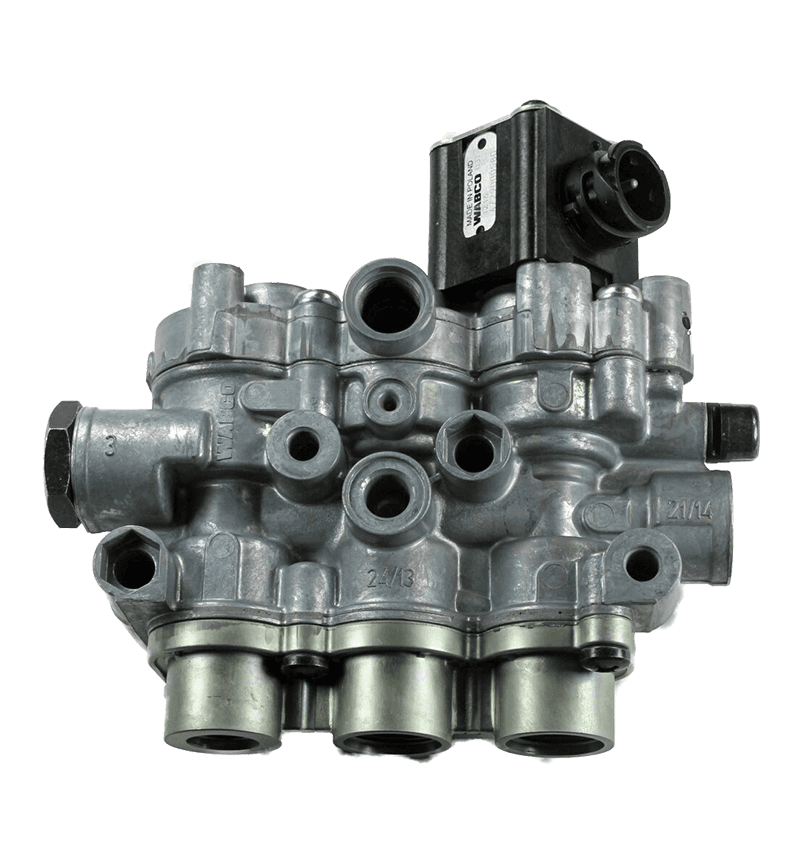
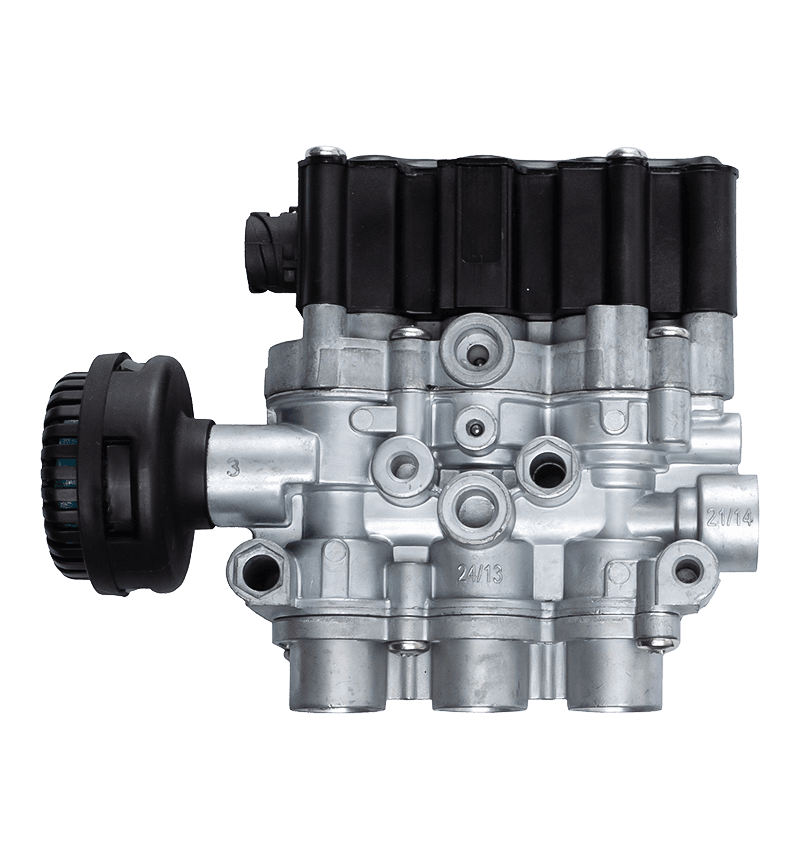
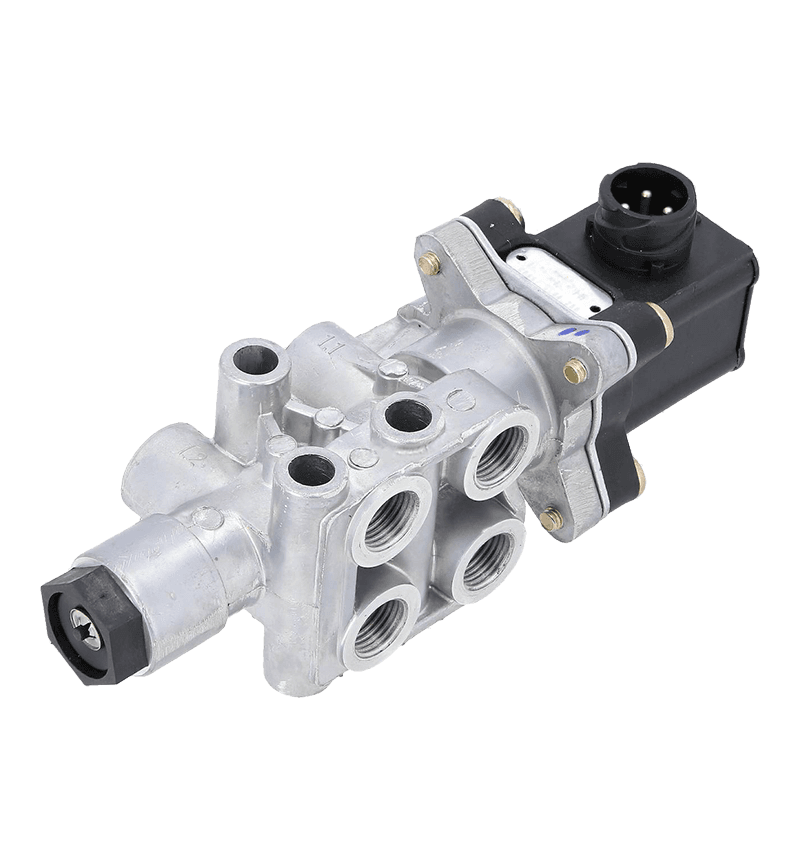
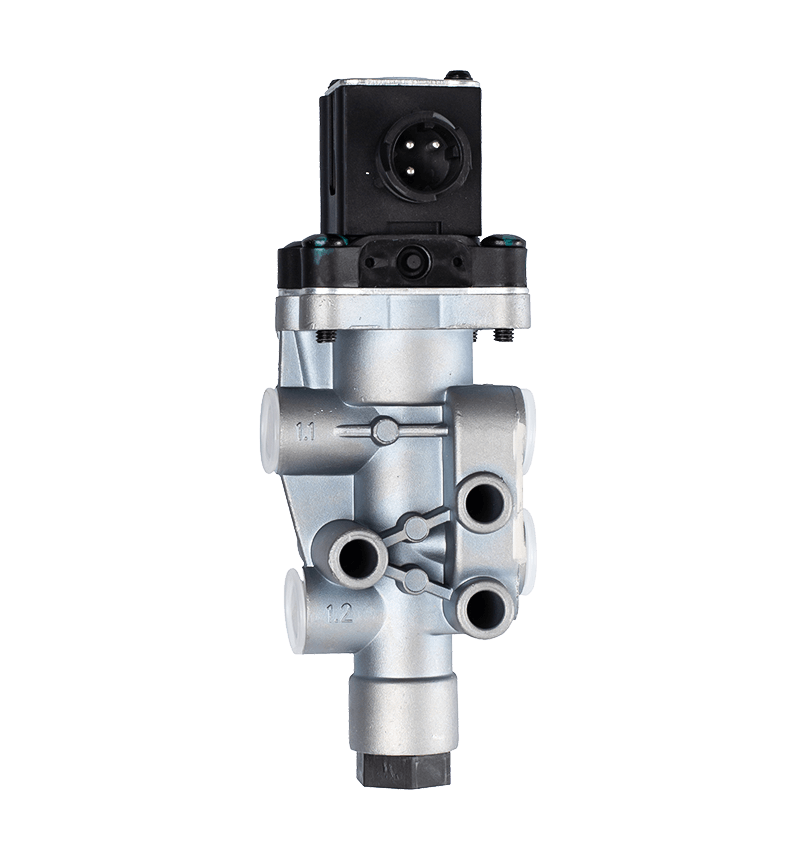
Gearbox valves play a crucial role in enhancing fuel efficiency in automotive and industrial applications by optimizing the performance of the gearbox, improving power transmission, and reducing energy losses.
Precise control of hydraulic fluid: In automatic or semi-automatic transmissions, gearbox valves regulate the flow of hydraulic fluid to control the operation of clutches, bands, and other components. By ensuring that the correct amount of fluid is delivered at the right pressure, these valves help achieve smooth shifting and reduce energy losses.
Efficient power transfer: A well-functioning gearbox valve ensures that the gears are engaged efficiently, which reduces friction and optimizes the power transfer from the engine to the wheels. This efficient energy transfer reduces the load on the engine, thereby improving fuel consumption.
Smooth and precise shifting: Gearbox valves control the timing and pressure of gear shifts in automatic transmissions. By enabling quicker, smoother shifts, they prevent unnecessary revving or over-revving of the engine. This reduces fuel wastage and allows the engine to operate more efficiently at optimal RPM levels.
Avoiding excessive engine load: Efficient valve operation ensures that gear changes occur at the ideal engine speed and load. Improper shifting (e.g., shifting too early or late) can increase fuel consumption, as the engine may have to work harder to compensate for poor gear engagement.
Torque converter control: In vehicles with automatic transmissions, the gearbox valve regulates the operation of the torque converter. By optimizing how torque is transferred from the engine to the transmission, it helps to reduce slippage, which in turn improves fuel efficiency.
Adaptive torque control: Some modern gearbox systems have valves that can adapt the torque distribution based on driving conditions. This ensures that the vehicle uses only the necessary amount of power, further enhancing fuel economy.
Minimizing clutch slippage: Gearbox valves regulate the application of the clutch in an automatic transmission. By minimizing clutch slippage during gear transitions, these valves reduce power losses. Clutch slippage is inefficient and increases fuel consumption, so minimizing it improves overall fuel economy.
Hydraulic pressure control: Gearbox valves help manage the hydraulic pressure within the system to ensure that all components function within optimal parameters, reducing the chance of fluid pressure loss, which can lead to inefficiency and increased fuel use.
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs): In CVTs, gearbox valves control the shift points and adjust the system to maintain the engine's optimal power band. By continuously adapting to the most fuel-efficient ratio between engine and wheel speed, CVTs contribute to better fuel efficiency. The precise control provided by gearbox valves ensures that the engine operates at its peak efficiency for varying driving conditions, without unnecessary fuel consumption.
Pressure regulation for load management: Gearbox valves maintain the correct pressure to ensure that the gearbox operates at its optimal capacity. Under high pressure, the system becomes less efficient, consuming more fuel. The valves regulate pressure to keep the system balanced and energy-efficient.
Temperature management: Overheating of the transmission can increase fuel consumption by reducing overall system efficiency. Gearbox valves contribute to maintaining the right temperature levels by controlling fluid flow, preventing overheating, and ensuring that the transmission remains within its optimal operating temperature range.

 English
English Español
Español