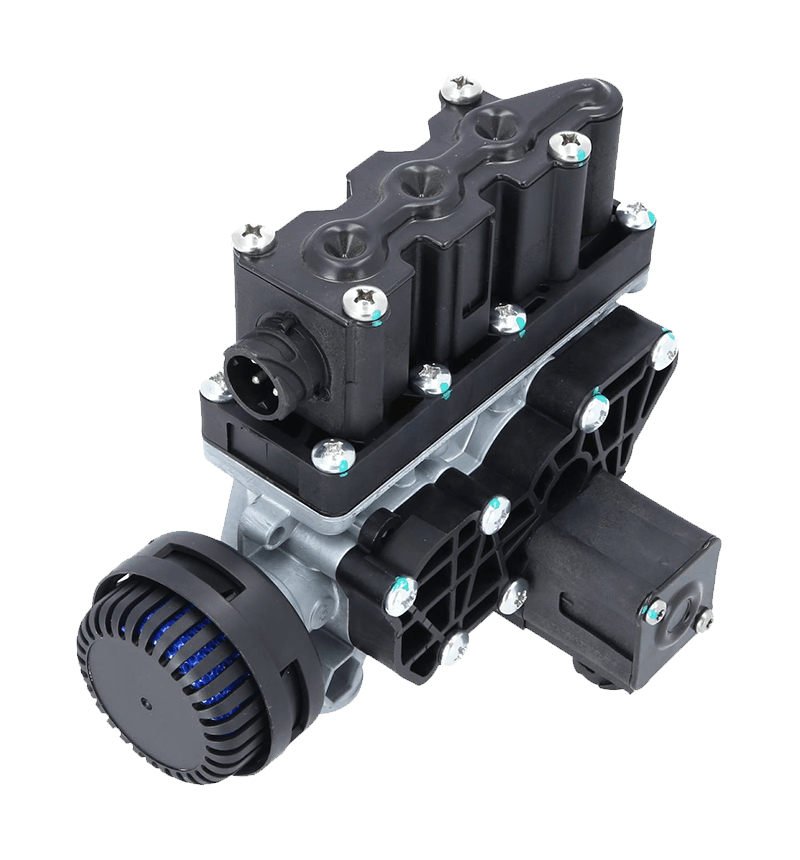
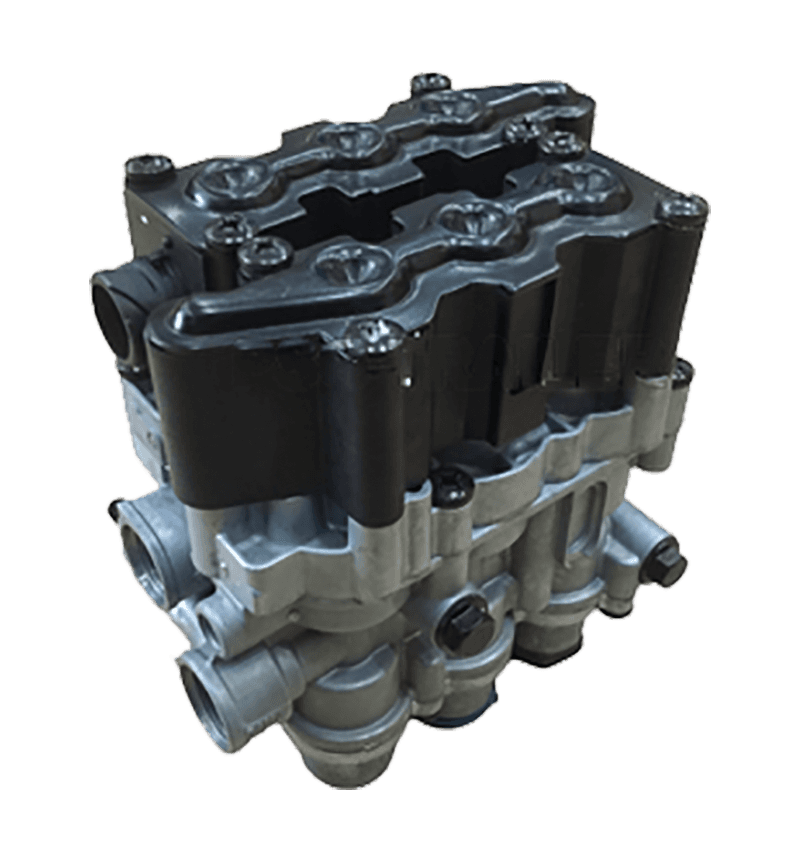
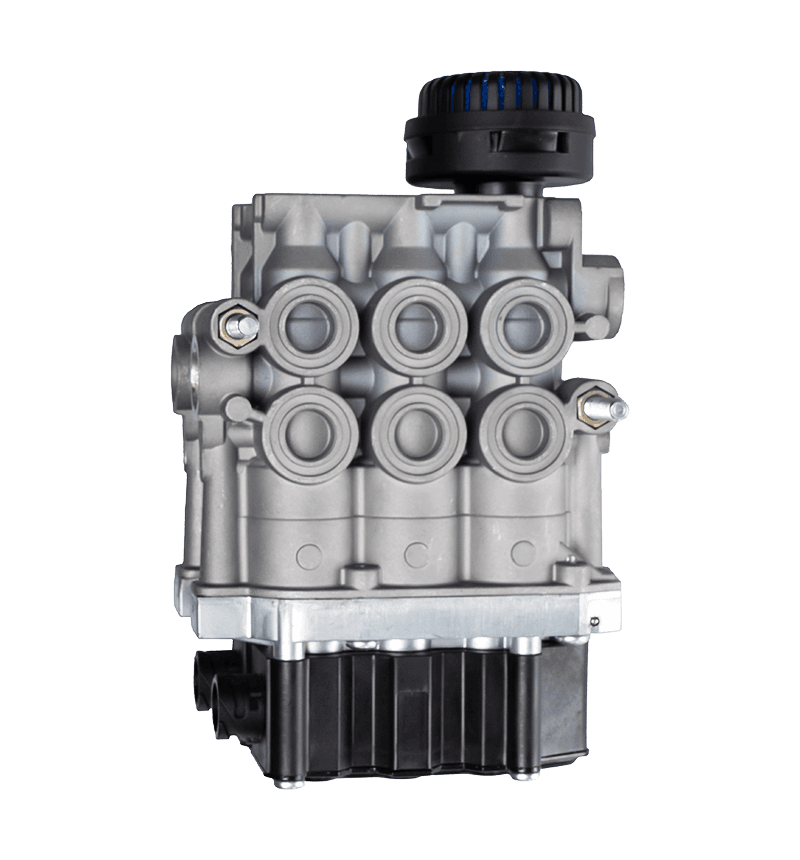
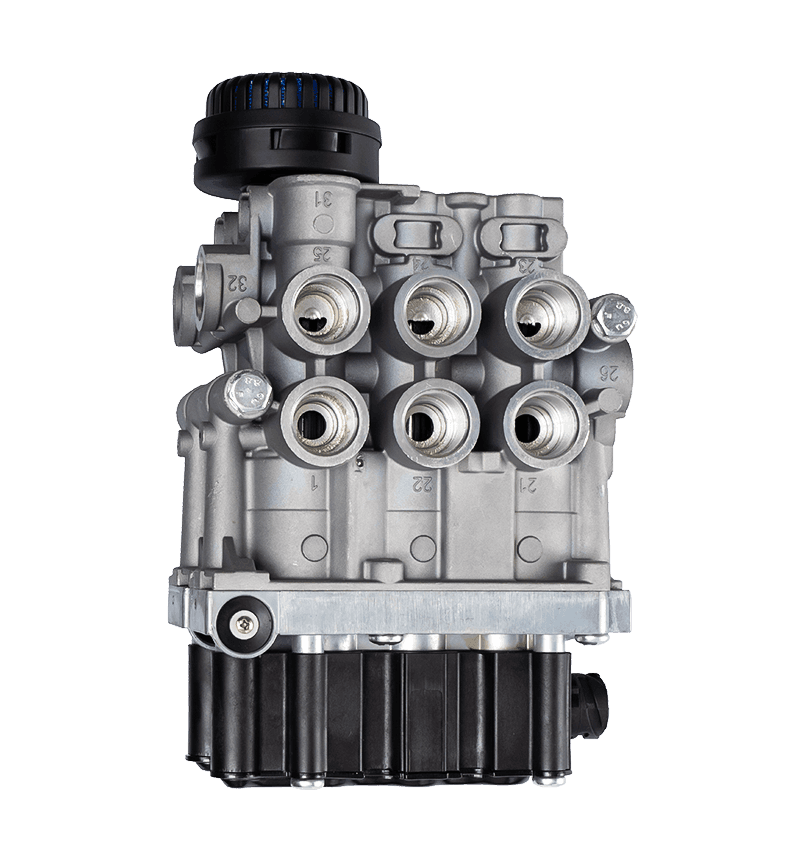
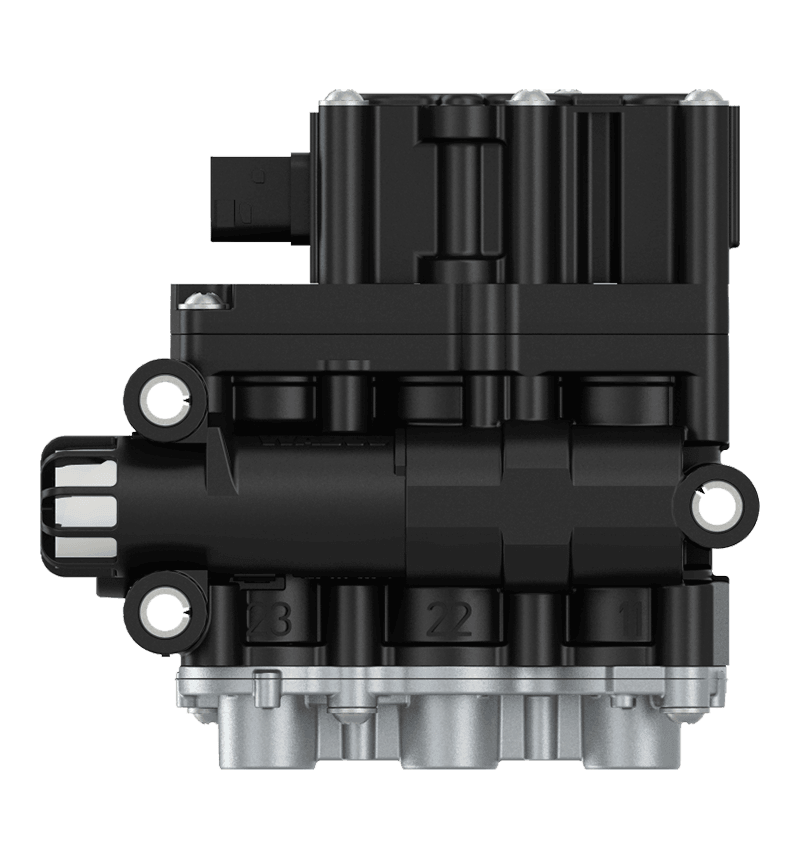
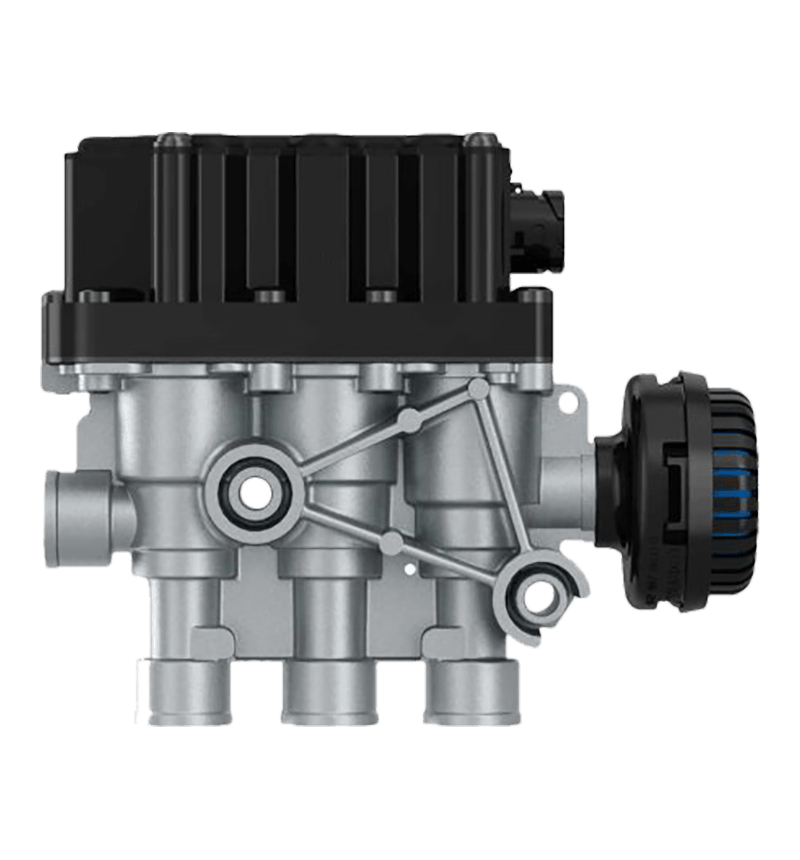
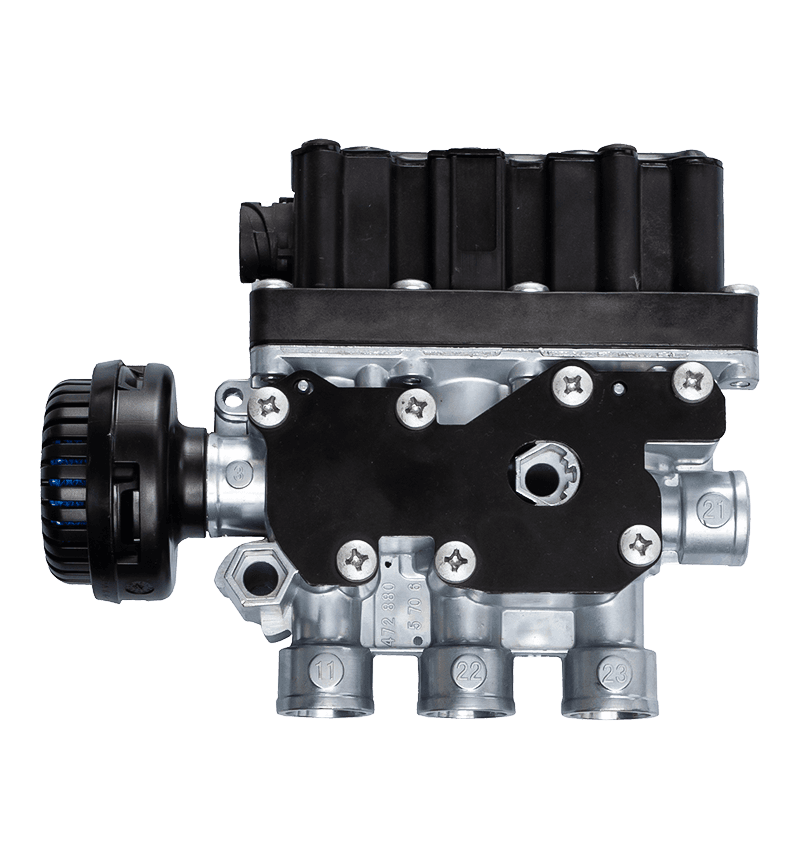
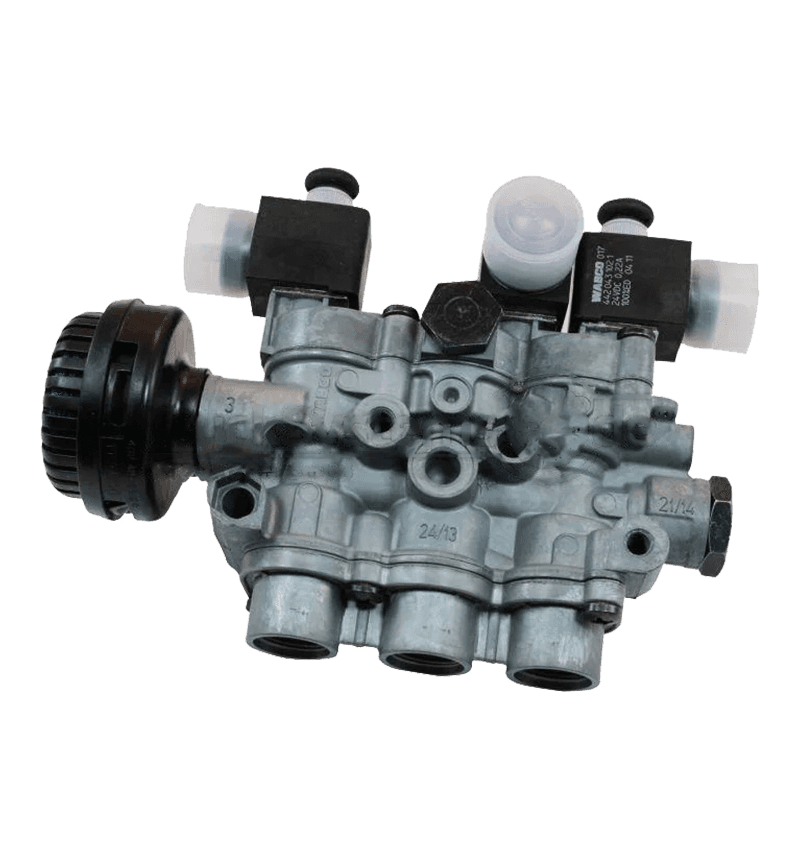
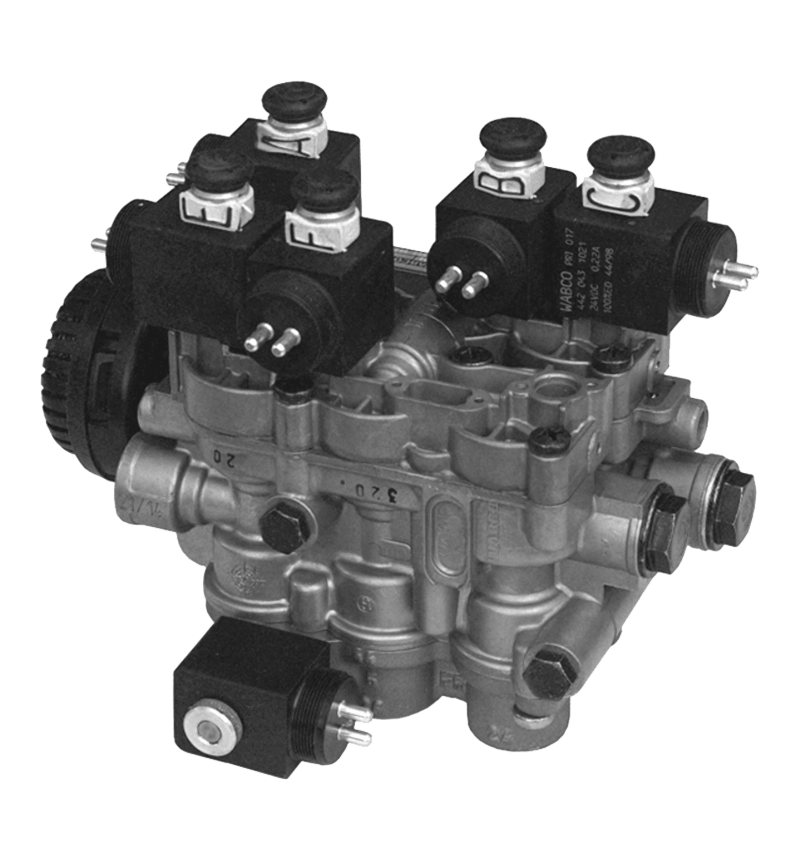
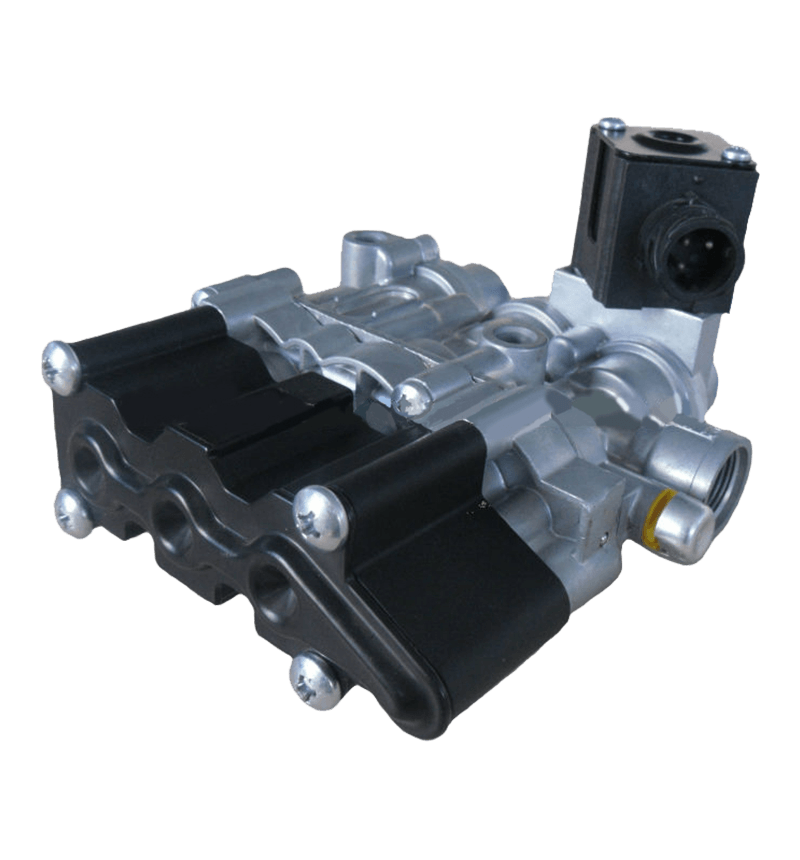
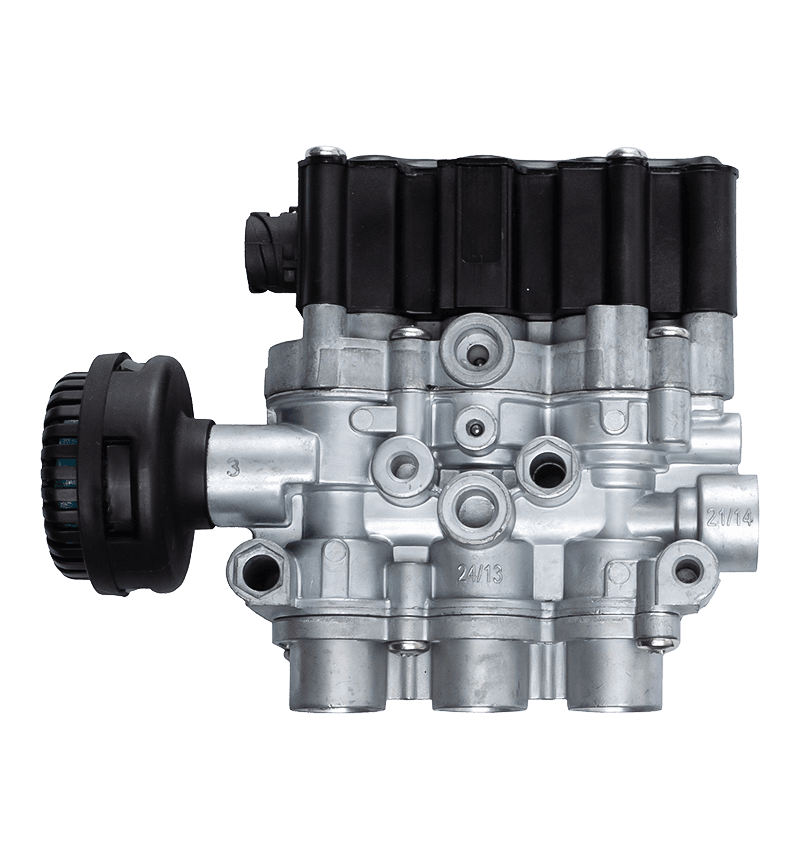
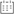Hand brake valves are integral components of a vehicle's braking system, particularly in commercial vehicles like trucks and buses. Their interaction with other components of the brake system is crucial for ensuring effective and safe braking. Here's how they interact:
Brake Actuators: Hand brake valves control the delivery of hydraulic or pneumatic pressure to brake actuators, which are devices that convert this pressure into mechanical force to apply the brakes. In pneumatic systems found in commercial vehicles, the hand brake valve directs compressed air to the brake chambers, causing the diaphragm or piston within the actuator to move. This movement then applies the brakes by pushing the brake shoes against the drum or engaging the brake pads with the rotor. The precision of this control is critical for effective braking performance, especially in holding the vehicle stationary.
Master Cylinder: In hydraulic brake systems, the master cylinder is a key component that generates hydraulic pressure when the brake pedal is pressed. The hand brake valve, particularly in systems where the parking brake is integrated, can interact with the master cylinder by isolating the hydraulic circuit used for the parking brake. This allows the parking brake to apply pressure to the brake lines independently of the main braking system, ensuring that the vehicle remains stationary even when the main brakes are not engaged.
Brake Lines: Brake lines are the conduits through which hydraulic fluid or compressed air travels from the hand brake valve to the brake actuators. The hand brake valve regulates the pressure within these lines, ensuring that the correct amount of force is transmitted to the brakes. In hydraulic systems, this involves managing the flow of brake fluid, while in pneumatic systems, it involves controlling the flow of compressed air. Proper regulation of this pressure is essential for consistent and effective braking.
Brake Shoes and Drums: In drum brake systems, the hand brake valve indirectly affects the brake shoes and drums by controlling the pressure that forces the brake shoes against the drums. When the hand brake is engaged, the valve either releases or directs pressure, causing the brake shoes to expand and press against the inner surface of the brake drum. This friction holds the vehicle stationary. The effectiveness of this interaction depends on the precise control of pressure by the hand brake valve, ensuring that the shoes firmly engage with the drum without causing excessive wear or damage.
Brake Calipers and Rotors: In disc brake systems, the hand brake valve regulates the hydraulic pressure that is sent to the brake calipers. The calipers then squeeze the brake pads against the rotors, creating the friction necessary to hold the vehicle in place. This interaction ensures that the parking brake system can effectively secure the vehicle. The hand brake valve must provide consistent pressure to the calipers to achieve reliable and stable braking performance, particularly on inclines or uneven surfaces.
Control Linkages and Cables: In mechanical hand brake systems, the hand brake valve may be part of a system that uses control linkages or cables to transmit force from the hand brake lever to the brake actuators. These mechanical connections must be precisely adjusted and maintained to ensure that the hand brake valve can effectively apply the brakes. Proper tension and alignment of the cables and linkages are crucial for the smooth operation of the hand brake system, preventing issues such as slack or excessive play that could compromise braking performance.

 English
English Español
Español