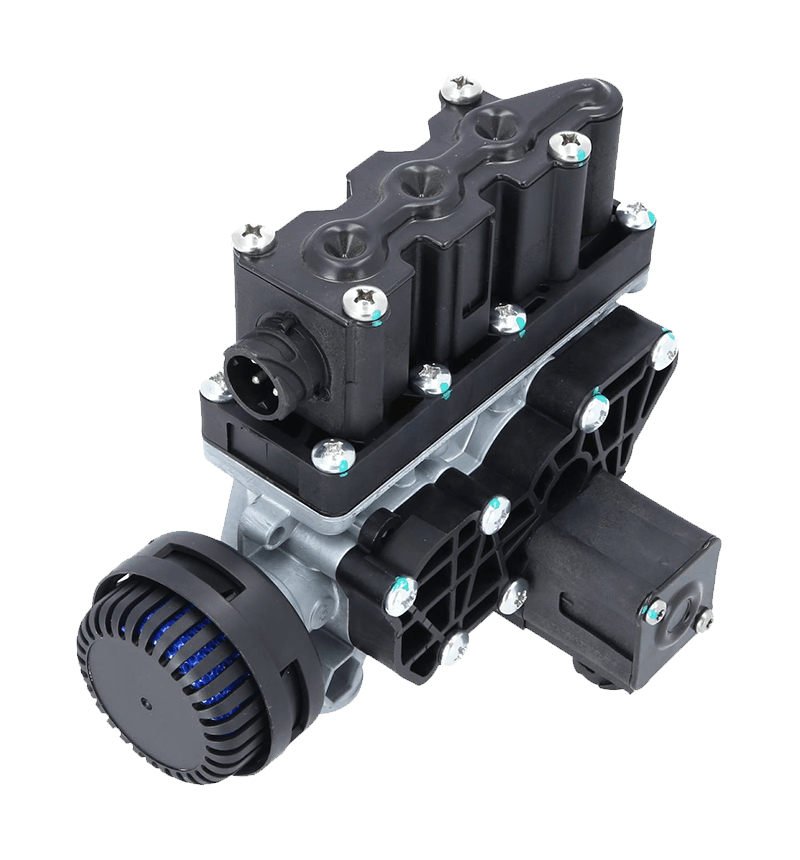
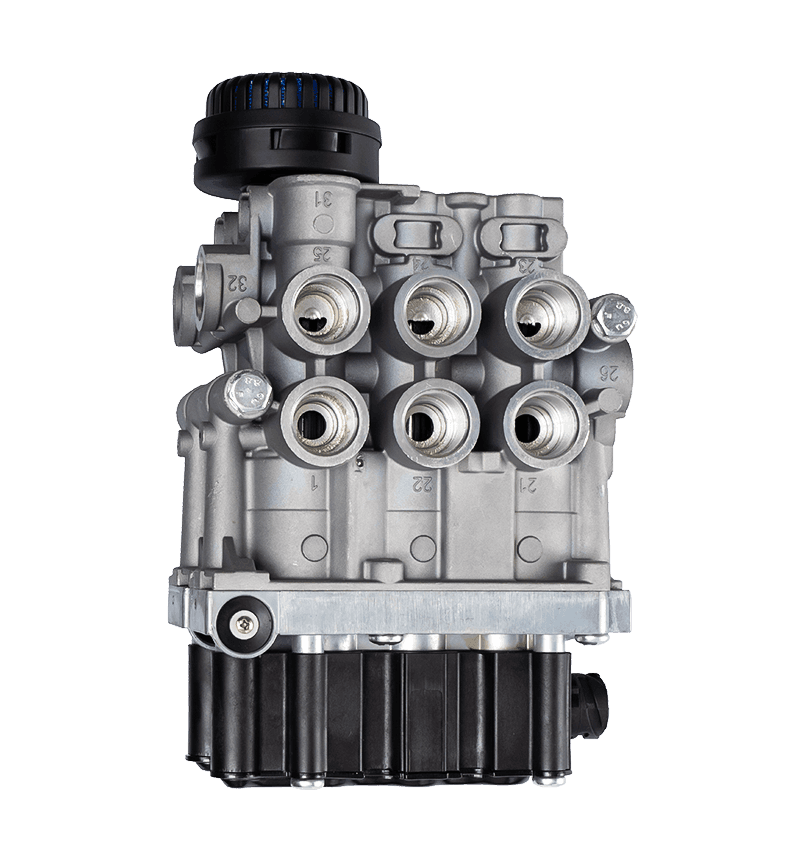
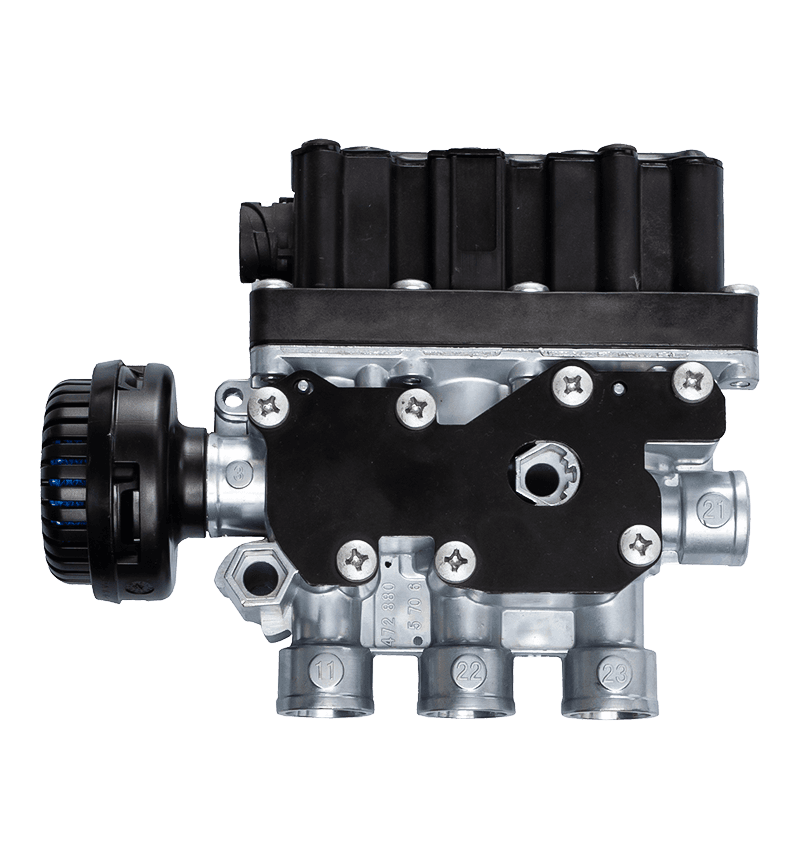
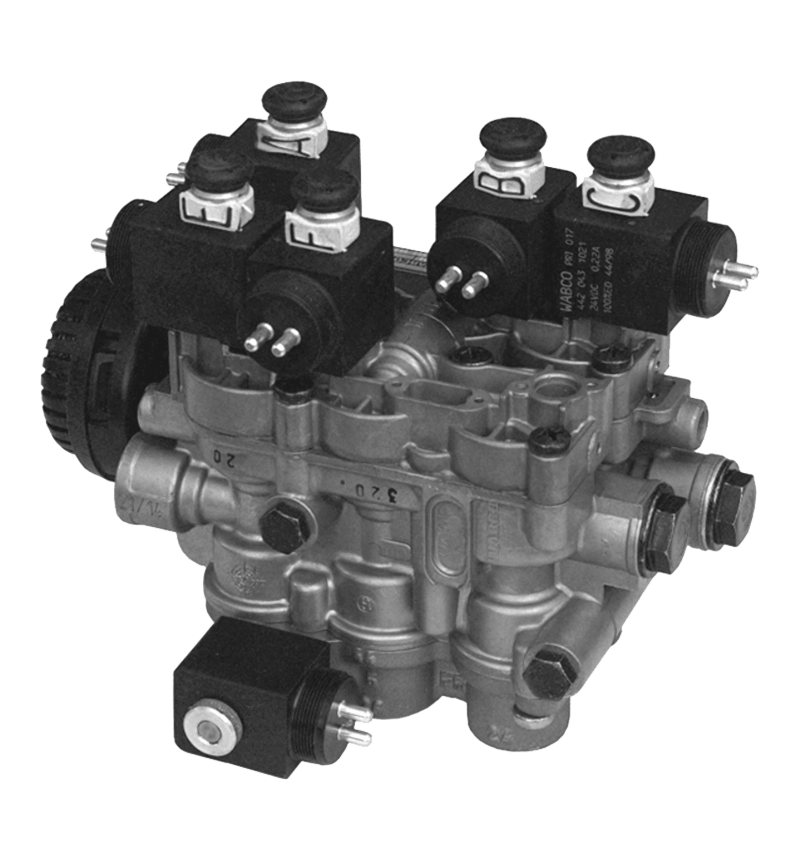
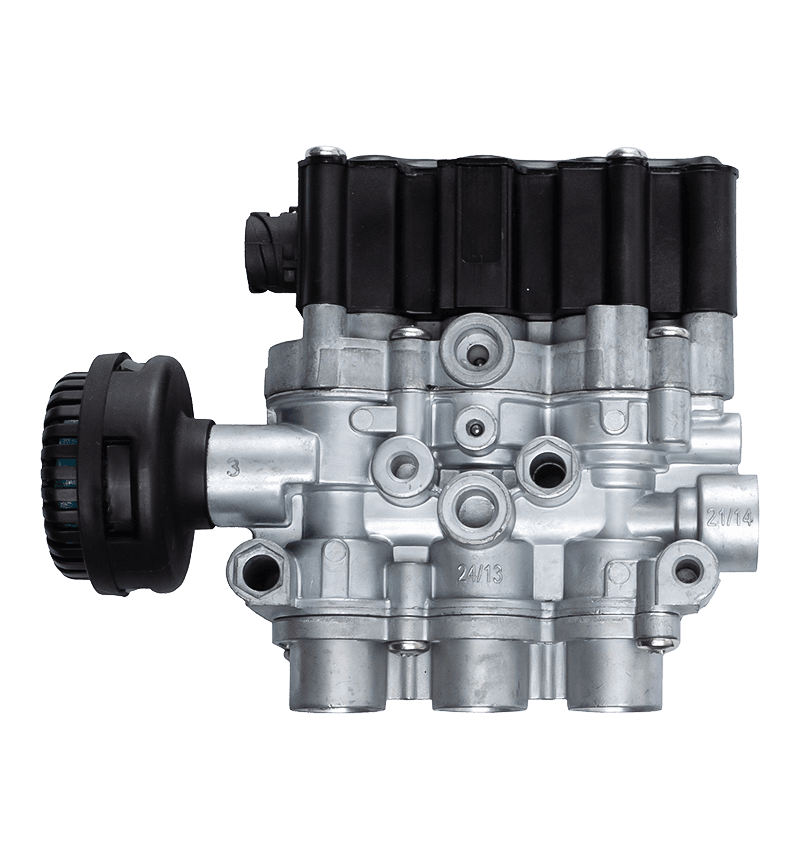
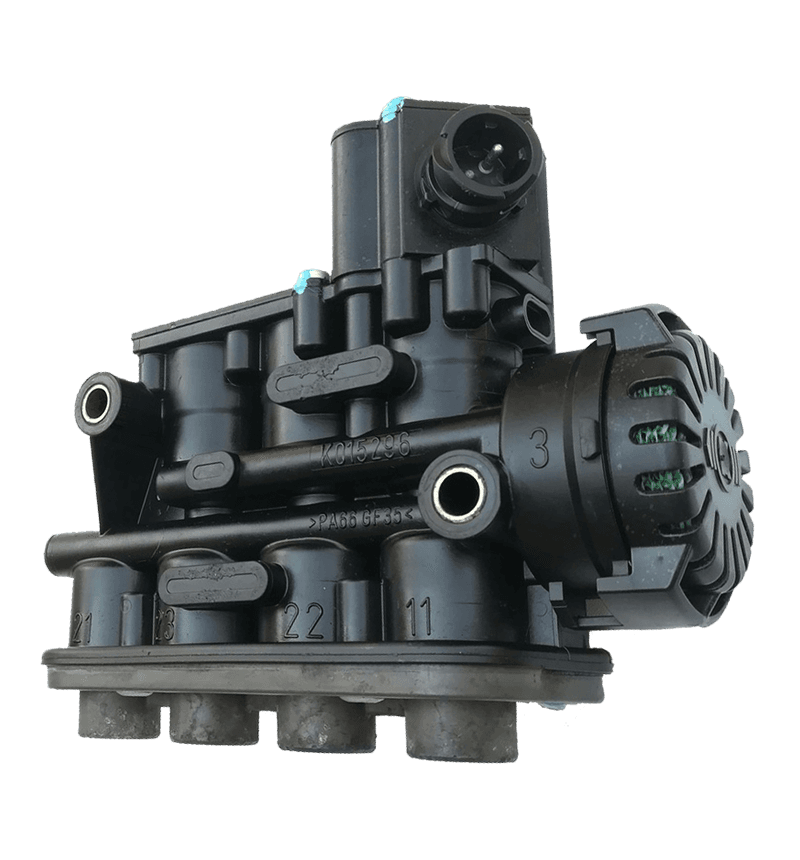
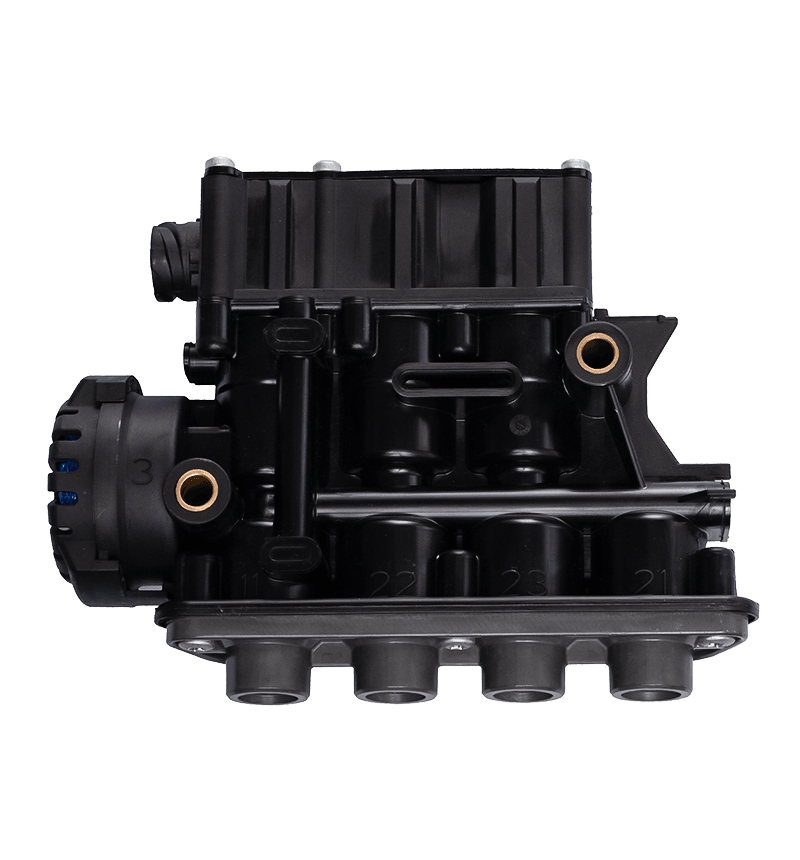
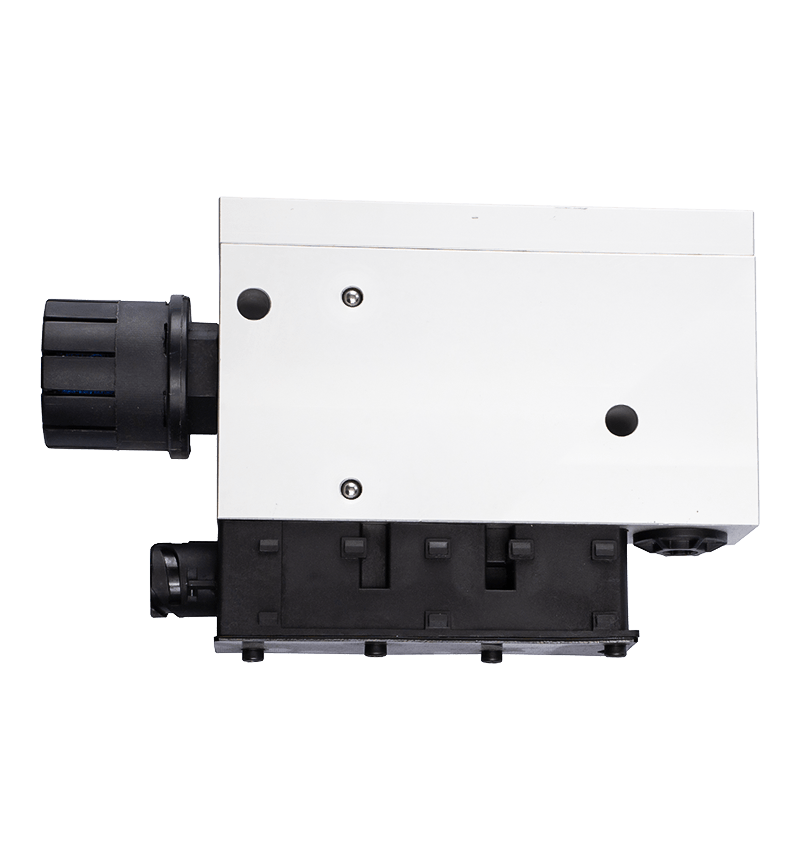
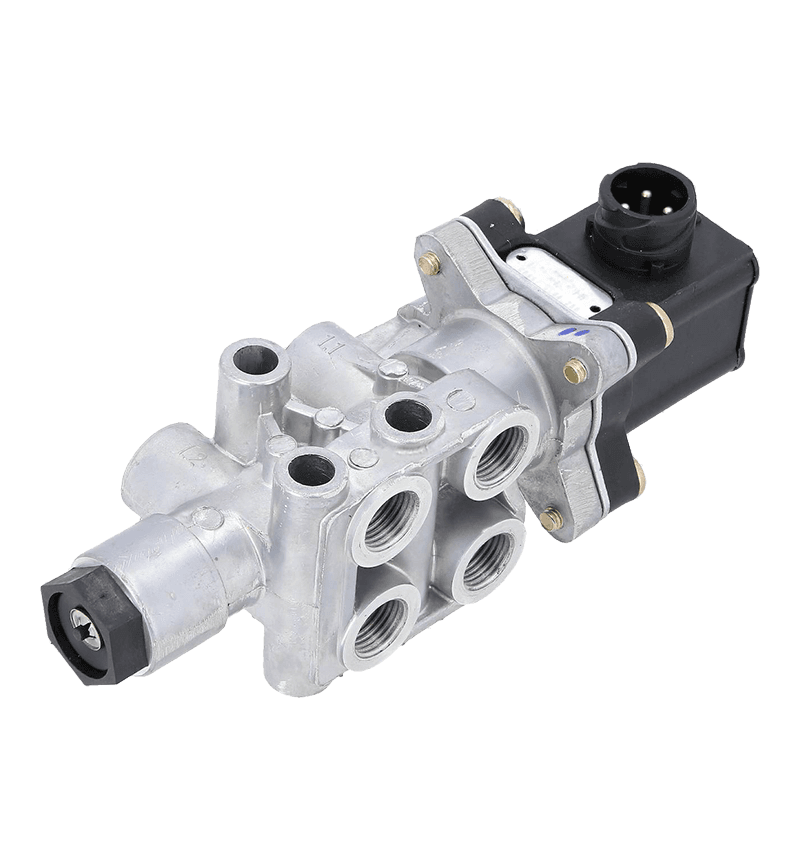
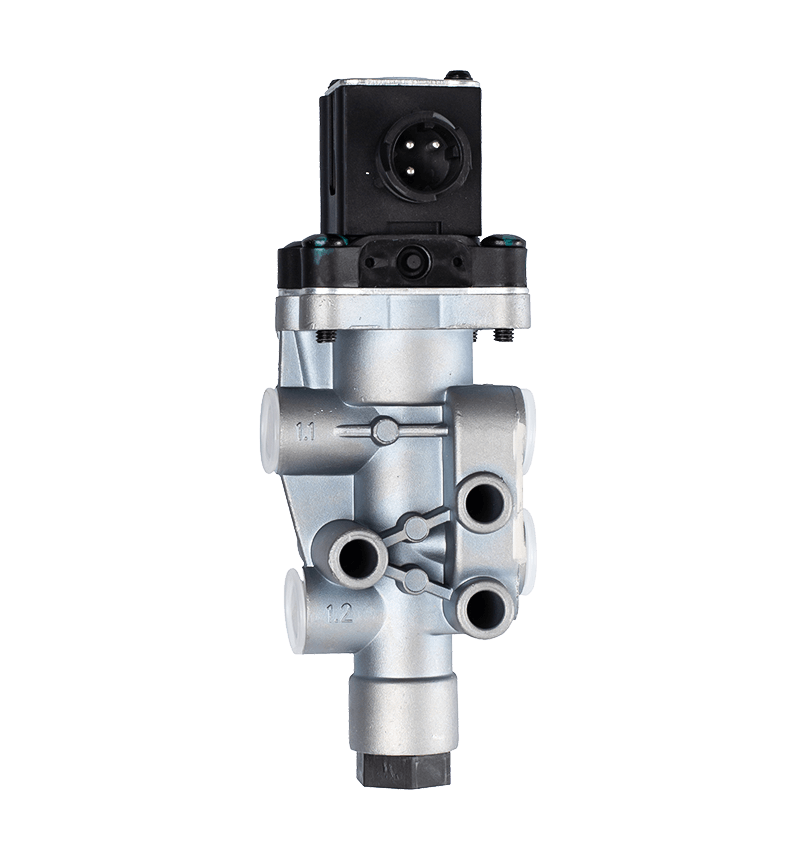
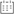The core of the redundancy principle lies in "backup" and "parallel work". In a redundant configuration of unloading valves, this means that the system contains not only a functioning unloading valve but also an additional spare unloading valve with the same or similar function. These backup unloading valves may be in a standby state under normal circumstances, but once the main unloading valve fails or cannot meet system needs, they can take over immediately to ensure system continuity and stability.
Advantages of redundant configurations
Improve system reliability: Redundant configuration significantly improves system reliability by increasing the system's fault tolerance. Even if the main unloading valve fails, the backup unloading valve can quickly take over, reducing system downtime and reducing losses caused by equipment failure.
Enhance system safety: In dangerous environments such as high pressure and high temperature, the failure of the unloading valve may cause serious safety accidents. Redundant configuration can ensure that in an emergency, the system can still maintain a certain safety margin and prevent the accident from expanding.
Optimize system performance: By working in parallel, redundantly configured unloading valves can share the system load and optimize system performance. During peak hours or special working conditions, the backup unloading valve can be put into operation and work in conjunction with the main unloading valve to improve the overall processing capacity of the system.
Easy maintenance and upgrade: Redundant configuration provides convenience for system maintenance and upgrade. When the main unloading valve needs to be maintained or upgraded, it can be switched to the backup unloading valve to ensure that the normal operation of the system is not affected.

 English
English Español
Español